Jewelry Education
Knowledge is the sparkle behind every confident purchase. Learn everything you need to know about diamonds, gemstones, and precious metals.

Diamond Shapes

Round Brilliant Cut (RBC)
The ultimate classic! The round cut diamond is the most popular diamond shape, representing approximately 75% of all diamonds sold. The round brilliant-cut was developed by Marcel Tolkowsky in 1919.

Princess Cut
The princess is traditionally a square cut or rectangular cut, with many variations. A princess cut diamond should always be set with prongs that protect the four corners.

Cushion Cut
Cushion-cut diamonds have rounded corners and feature larger facets to increase their fiery brilliance. They combine a square cut with rounded corners, much like a pillow (cushion).

Marquise Cut
The Marquise cut originated in the 1700s and may have been named after the Marquise de Pompadour, a mistress of King Henry XV.

Pear Cut
The Pear cut looks like a rain or tear drop, pointed at one end. It may or may not have a large flat or table facet in the center of the stone. They are created by combining a round and marquise shape diamond shapes.

Heart Cut
The romantic Heart shape is shaped like a heart. The corners of this diamond may show the color if you are buying a color grade diamond.

Oval Cut
The Oval cut is oval in shape and is covered with rectangular facets. Rounded on both sides. The oval cut optimizes the carat weight and elongates the finger.

Emerald Cut
The Emerald cut is a square or rectangular cut with the corners cut diagonally. Emerald cut diamonds produce a hall-of-mirrors effect, with the interplay of light and dark planes.

Radiant Cut
Trimmed corners are the signature of the radiant cut diamonds, making it a popular and versatile choice for jewelry. The radiant cut diamond is the first square cut second only being the princess.
Diamond Quality (4C's)

Cut
Cut can make a diamond look bigger. It means that you get a free boost in the other aspects of the 3Cs (color, carat and clarity) just by having a better cut. The cut of a diamond refers not only to the shape of the diamond and number of facets, but also to the quality of the cut.

Color
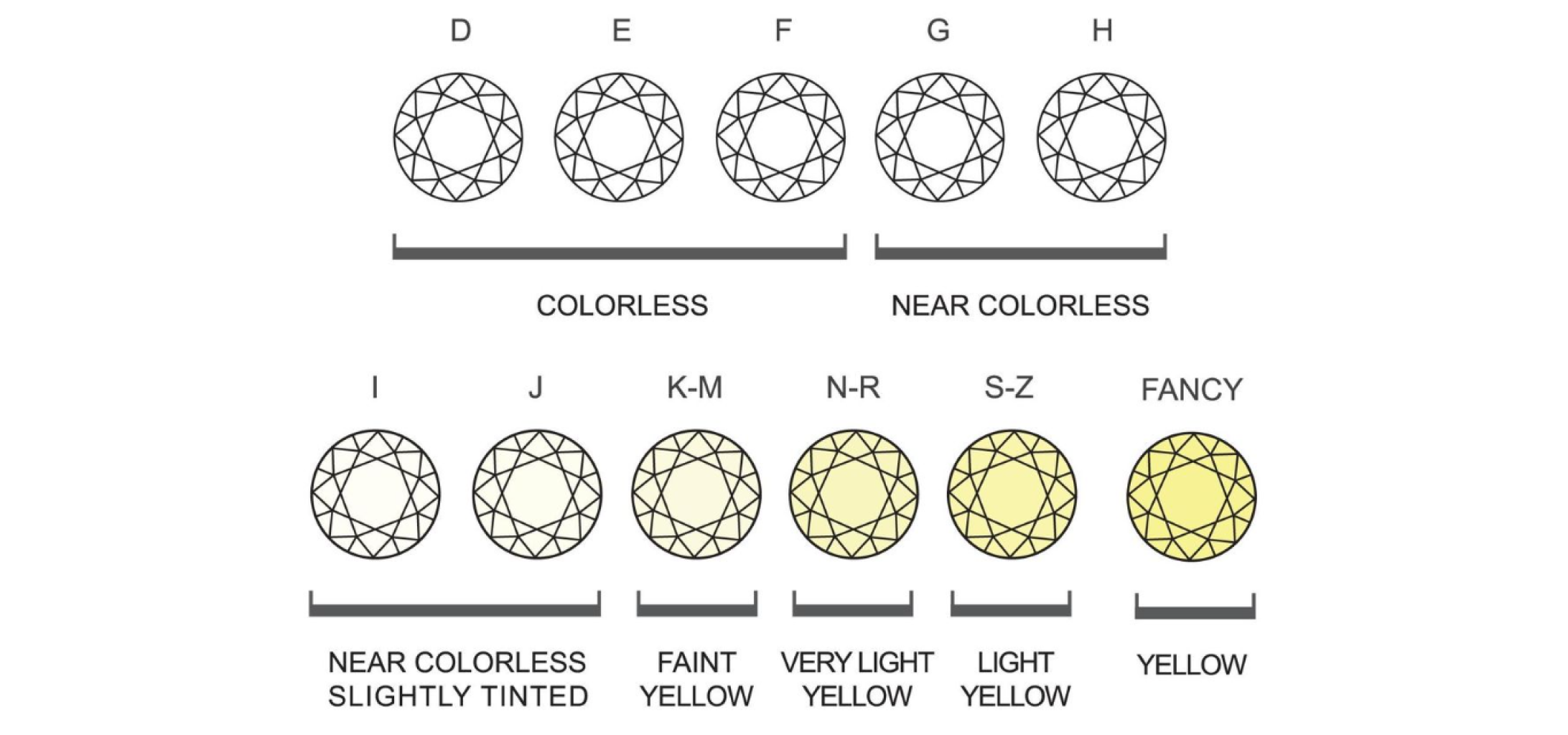
Colorless diamonds are generally more valuable and commonly used in jewelry as they have better reflective qualities. For diamonds in the colorless range (D-F), they are priced at a higher premium. Personally, these are the gemstones I would love to get my hands on.

Carat
Carat is used to describe the weight of diamonds. Generally the larger the stone the greater value. Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. Each carat can be subdivided into 100 'points.' This allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place.

Clarity
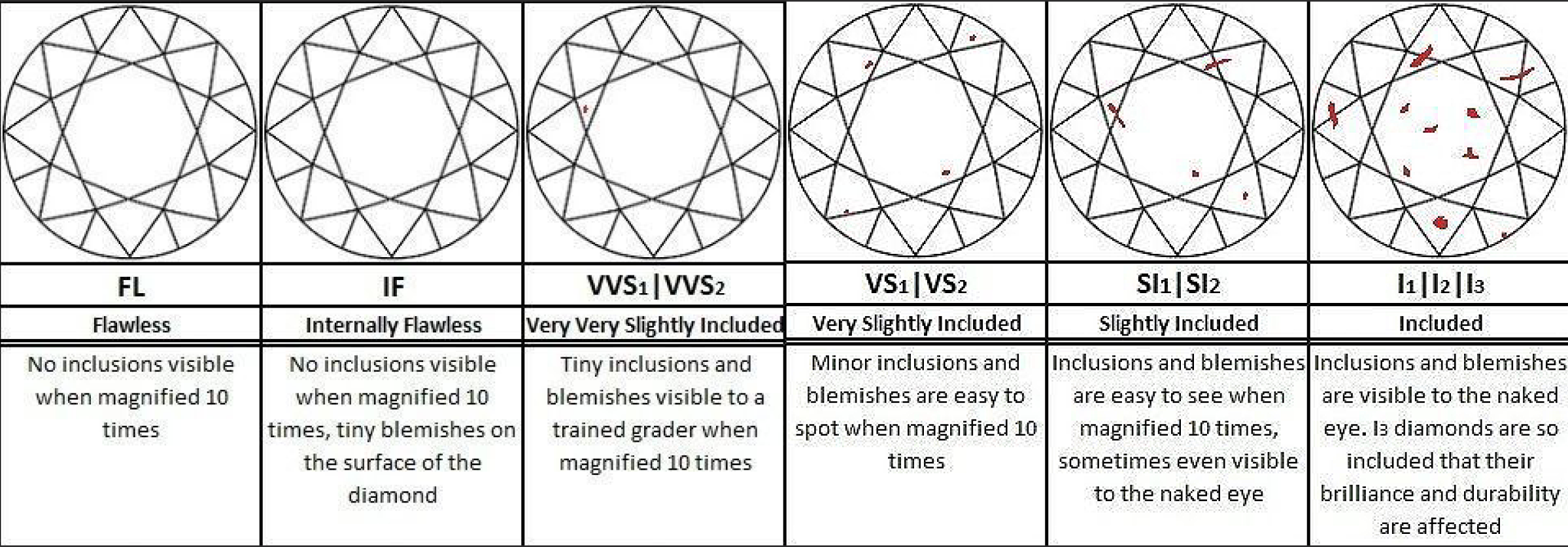
Clarity measures the imperfections. The purest, the higher its value. GIA considers the number, size, color, reflectivity, and position of every flaw visible under 10x magnification. In a certified diamond, the cracks are charted on the certificate and act as a fingerprint for identifying a particular stone.
Cut Chart

Color Chart
Clarity Chart
A Rejection Tool
The Holloway Cut Adviser is a computer algorithm for scoring the cut of Round Brilliant diamonds.
The score represents a diamond's potential visual performance. Visual performance is graded in terms of desirable characteristics such as potential Light Return, Fire, Scintillation, and Spread. Taking these factors into account, an overall score is produced for a diamond.
The HCA is intended to be a Diamond Elimination Tool for filtering out diamonds that lack visual performance and exhibit less desirable levels of light return — not as a diamond selection tool.
The free simulation software can be found here: Holloway Cut Adviser.
Considering all the facts around the algorithm, one can say that the HCA score is a very useful free tool. It can definitely help eliminate what not to buy; however, selecting a lovely diamond should not depend entirely on it. Beauty of a diamond is in the eye of the beholder and cannot be judged merely by numbers. Every diamond is unique.
